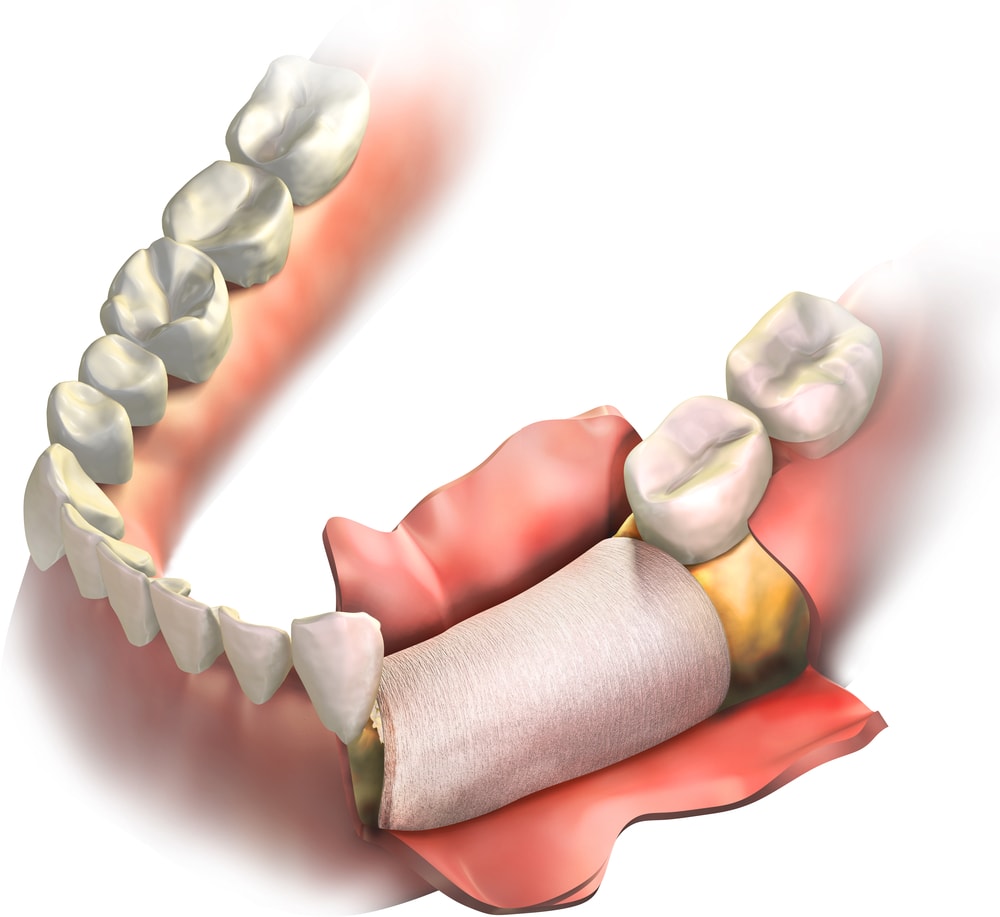
Exploring the realm of bone grafting in the context of dental procedures unveils a crucial aspect often overlooked in oral health discussions. Understanding the intricacies of bone grafts can shed light on the significance they hold in restorative dentistry and their pivotal role in enabling various dental interventions.
Delving into the motivations behind bone loss and the diverse types of grafts available can provide a comprehensive perspective for both patients and practitioners. As we unravel the nuances of bone grafting, a deeper comprehension emerges, offering a gateway to enhanced insights that can influence dental treatment outcomes significantly.
Importance of Bone Grafting
Bone grafting plays a crucial role in restoring proper bone structure and functionality in dental procedures. It is of paramount importance in maintaining optimal dental health by addressing issues related to bone loss. When a tooth is lost or extracted, the surrounding bone can begin to deteriorate over time. This bone loss can not only affect the aesthetics of the face but also compromise the ability to receive dental implants or other restorative treatments.
Dental bone grafting is a procedure designed to stimulate bone formation and promote bone growth in areas where it has been compromised.
Ensuring healthy bone structure is essential for the success of various dental procedures. Without an adequate amount of bone to support implants or other dental prosthetics, patients may face challenges in achieving long-lasting results. By undergoing bone grafting, individuals can enhance the strength and density of their jawbone, providing a solid foundation for future dental work.
Reasons for Bone Loss
Deterioration of the jawbone can occur due to various underlying factors, impacting the structural integrity necessary for supporting dental implants and prosthetics effectively. One of the primary causes of bone loss in the jaw is periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease. This condition leads to the destruction of the tissues surrounding the teeth, including the alveolar bone, which is crucial for the stability of teeth. When left untreated, periodontal disease can progress to a point where it causes significant bone resorption, resulting in a weakened jawbone structure.
Another reason for bone loss in the jaw is the presence of diseased bone. This can occur due to infections, trauma, or other medical conditions that affect the health of the bone tissue. In situations where the bone is already compromised, the extent of bone loss can be severe, making it challenging to support dental implants without additional intervention such as bone grafting.
Maintaining healthy bone in the jaw is essential for overall oral health and the success of dental procedures. Understanding the reasons behind bone loss, such as periodontal disease and diseased bone, highlights the importance of timely intervention to prevent further deterioration. By addressing these underlying issues and considering treatments like periodontal bone grafts, it is possible to restore the integrity of the jawbone and create a stable foundation for dental implants.
Types of Bone Grafts
An essential aspect to consider when addressing bone loss in the jaw is understanding the various types of bone grafts available for dental procedures. These bone grafts play a crucial role in restoring bone volume, promoting bone healing, and preparing the jaw for dental implants or other restorative procedures.
One common type of bone graft is the socket graft, which is performed at the site of a recently extracted tooth to preserve the bone and prevent resorption. Ridge augmentation is another technique that involves adding bone to the jaw to rebuild its shape and size for implant placement. Sinus lifts are specialized bone graft procedures that increase bone height in the upper jaw to support dental implants in the posterior region.
Dental bone graft surgery can involve different sources of bone material. Autogenous bone grafting uses the patient’s bone from another site in the body, providing the most natural and successful integration. Synthetic bone grafts, on the other hand, are man-made materials that mimic bone properties. Allogenic bone is sourced from a bone bank and is used when a large amount of bone graft is needed.
Alveolar ridge preservation is a technique to prevent bone loss after tooth extraction, maintaining the natural shape of the jaw. Understanding these types of bone grafts is essential for dental professionals to choose the most appropriate method for each patient’s specific needs and ensure successful outcomes.
Bone Graft Procedure Overview
A comprehensive understanding of the process involved in bone graft procedures is crucial for dental professionals to ensure successful outcomes for patients undergoing treatment. A bone graft procedure is a surgical method used to replace or restore missing bone tissue by transplanting bone tissue, either from the patient’s own body (autograft) or from a donor (allograft). The choice of bone graft material can include natural bone, synthetic materials, or a combination of both, depending on the specific needs of the patient and the complexity of the procedure.
Bone graft surgery typically involves several steps. First, the dental surgeon will make an incision in the gum tissue to access the area where the bone graft is needed. Then, the bone grafting material is placed and secured in position. The body will gradually replace the bone graft material with natural bone over time through a process called bone graft healing.
There are different types of bone grafts, including socket preservation grafts, block bone grafts, and sinus lifts, each tailored to address specific dental conditions. The success of a bone graft procedure relies on proper patient care post-surgery, which will be discussed in the next subtopic, ‘Recovery After Bone Graft’. Understanding the intricacies of bone graft procedures is essential for dental professionals to provide optimal care and support for their patients throughout the treatment process.
Recovery After Bone Graft
Following a bone graft procedure, patients must diligently adhere to post-operative care instructions to promote optimal healing and successful recovery. The recovery after a bone graft is a crucial phase that requires patience and commitment to ensure the best possible outcome. Understanding the bone graft healing stages can help individuals manage their expectations and actively participate in the healing process.
The recovery time after a bone graft varies depending on the individual’s overall health, the size of the graft, and the specific location where the graft was performed. Typically, it takes several months for the bone graft to integrate fully and for the new bone mass to develop into a stable foundation for dental implants or other restorative procedures. During this period, the body’s healing capacity plays a significant role in successful bone healing.
To promote faster healing and efficient bone repair, patients are advised to follow a nutritious diet, avoid smoking, practice good oral hygiene, and attend all follow-up appointments with their dental provider. These measures can help reduce the risk of complications and support the body’s natural ability to regenerate bone tissue. By prioritizing proper care and attention during the recovery after a bone graft, patients can enhance their chances of a successful outcome and enjoy improved oral health in the long term.
Risks and Complications
After undergoing a bone graft procedure, it is essential to be aware of the potential risks and complications that may arise during the healing process. While bone grafts are generally safe and effective, there are some risks associated with this dental procedure. One potential risk is the development of complications such as infection, which can occur at the graft site. In some cases, the body may reject the graft material, leading to immune reactions and potential side effects. Patients may also experience severe pain following the procedure, which can be managed with pain medication prescribed by the dentist.
Another factor to consider is dental implant risks. If the bone graft is being done in preparation for a dental implant, there is a possibility of the implant not integrating properly with the grafted bone, leading to implant failure. Additionally, patients with dental anxiety may find the bone graft procedure to be stressful, potentially affecting the healing process.
It is important for patients to follow post-operative care instructions diligently to minimize the risk of complications. In some cases, additional risks may be present depending on the individual’s overall health and the need for subsequent restorative procedures. Consulting with a qualified dental professional can help address any concerns and ensure a successful bone graft healing process.
Bone Graft Success Factors
Achieving optimal outcomes in bone graft procedures hinges significantly on meticulous pre-operative planning and precise surgical technique. Several key factors contribute to the success of bone graft procedures, ensuring the reconstruction of bone tissue and providing a stable base for implant placement.
One crucial aspect is the selection of appropriate bone material. Utilizing high-quality bone graft material enhances the body’s acceptance of the graft, promoting the growth of healthy bone tissue. The chosen material should also possess the necessary properties to support bone-building cells and facilitate bone reconstruction effectively.
Moreover, the surgical technique employed plays a vital role in the success of bone graft procedures. The surgeon’s skill in creating a strong foundation for the graft, ensuring proper placement, and securing the graft in position influences the overall success of the procedure. A stable base is essential for long-term success, enabling the integration of the bone graft with the surrounding tissues.
Key Takeaways
Bone grafting is a crucial procedure in dental surgery to restore bone structure for dental implants.
Understanding the importance of bone grafting, reasons for bone loss, types of bone grafts, the procedure overview, recovery process, risks, and success factors are essential for both patients and dental professionals.
By following proper protocols and considering individual factors, the success of bone grafting can be greatly improved.
In conclusion, bone grafting is a vital step in dental surgery to ensure the success of dental implants by restoring bone structure. To fully grasp the significance of bone grafting, understanding various aspects such as reasons for bone loss, types of bone grafts, the procedure overview, recovery process, risks, and success factors is essential for patients and dental professionals alike. By adhering to correct protocols and considering individual factors, the outcome of bone grafting can be significantly enhanced. For those seeking expert dental care in bone grafting and other procedures, Toothsome Chatswood in Chatswood, NSW, is a trusted destination. Contact Toothsome Chatswood today to schedule a consultation and take the first step towards a healthier smile.